Very efficient organo-zinc scorpionates for CO2 fixation into a variety of cyclic carbonates: synthesis, coordination ability and catalytic studies†‡
Abstract
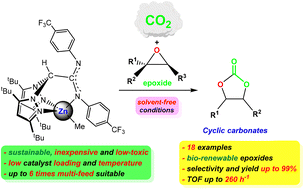
The fixation of CO2 mediated by metal-based catalysts for the production of organic molecules of industrial interest such as cyclic carbonates is urgently required under green and eco-friendly conditions. Herein, we describe the easy preparation of sterically demanding scorpionate ligands bearing different electron-withdrawing groups, and their coordination ability for the preparation of robust zinc-based mononuclear complexes of the type [ZnMe(κ3-NNN′)] (4–6). These complexes, in combination with co-catalysts comprising larger ionic radius-based halides such as tetra-n-butylammonium, functioned as very active and selective catalysts for CO2 fixation into five-membered cyclic carbonates. These studies have led to the development of sustainable, inexpensive, and low-toxicity systems formed by 4–5 and Bu4NBr for the cycloaddition of CO2 into epoxides under very mild and solvent-free conditions, reaching very good to excellent conversions (TOF = 260 h−1). Moreover, these bicomponent systems show a broad substrate scope and functional group tolerance, including mono- and di-substituted epoxides, as well as bio-renewable diepoxides. Very interestingly, these are the first zinc-based systems reported to date for the successful transformation of the very challenging tri-substituted terpene-derived cis/trans-limonene oxide, whose reaction proceeds with high stereoselectivity to the formation of the bicyclic trans-limonene carbonate. Additionally, these bicomponents can be efficiently used up to six times without significant loss of activity. Kinetic investigations confirmed that the reaction shows an apparent first-order dependence on the catalyst and co-catalyst concentrations, which indicates an intramolecular monometallic mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...