Pd/N, S co-doped activated carbon as a highly-efficient catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of meropenem†
Abstract
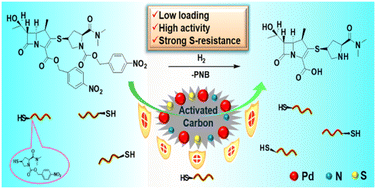
N, S co-doped active carbons (ACs) were synthesized and utilized as supports to prepare palladium/activated carbon (Pd/C) catalysts. Characterization of the as-prepared supports suggested that the variety of surface functional groups impacted Pd nanoparticles (NPs) with regard to particle size, chemical state, and dispersion. N, S co-doped activated carbon-supported Pd nanoparticles modified with 3 wt% sulfur with a reduced size distribution of approximately 1.81 nm exhibited substantially enhanced activity for the one-pot synthesis of meropenem and provided a higher meropenem yield compared to other Pd/C catalysts. The nitrogen and sulfur groups provided efficient anchoring sites to facilitate Pd NPs dispersion onto the AC surface, which facilitated electron transformation between the supports and the Pd nanoparticles, and contributed to forming relatively electron-deficient, ultra-low size Pd NPs, thereby improving the anti-poisoning performance of Pd/C catalysts, leading to high hydrogenation activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...