Photo-oxidation reaction of tert-butyl chloride with OH radicals and Cl atoms in the troposphere and its implications†
Abstract
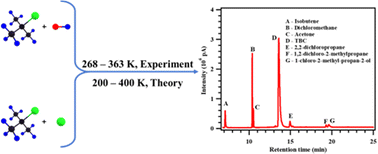
In the present work, the temperature-dependent kinetics for the reaction of tert-butyl chloride (TBC) with OH radicals and Cl atoms were determined experimentally between 268 and 363 K, and theoretically between 200 and 400 K. Pulsed laser photolysis-laser induced fluorescence (PLP-LIF) and relative rate (RR) methods were used to obtain the rate coefficients for the reaction of TBC with OH radicals and Cl atoms, respectively. The Arrhenius equations 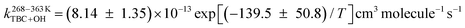 and
and 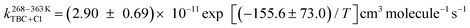 were obtained for both reactions based on the experimentally measured rate coefficients. The theoretical rate coefficients were determined at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-31+G(d,p) level for the reaction of TBC with OH radicals and at the CCSD(T)/cc-pVDZ//MP2/6-311+G(d,p) level for the reaction with Cl atoms with incorporated tunnelling corrections. The product analysis of both reactions in the presence of oxygen (O2) was carried out, and a degradation pathway for TBC was proposed. The potential implications of these reactions in the atmosphere were discussed using the obtained kinetic parameters.
were obtained for both reactions based on the experimentally measured rate coefficients. The theoretical rate coefficients were determined at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//M06-2X/6-31+G(d,p) level for the reaction of TBC with OH radicals and at the CCSD(T)/cc-pVDZ//MP2/6-311+G(d,p) level for the reaction with Cl atoms with incorporated tunnelling corrections. The product analysis of both reactions in the presence of oxygen (O2) was carried out, and a degradation pathway for TBC was proposed. The potential implications of these reactions in the atmosphere were discussed using the obtained kinetic parameters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...