Nanobead handling on a centrifugal microfluidic LabDisk for automated extraction of cell-free circulating DNA with high recovery rates†
Abstract
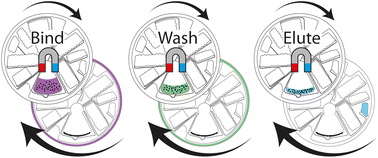
cfDNA is an emerging biomarker with promising uses for the monitoring of cancer or infectious disease diagnostics. This work demonstrates a new concept for an automated cfDNA extraction with nanobeads as the solid phase in a centrifugal microfluidic LabDisk. By using a combination of centrifugal and magnetic forces, we retain the nanobeads in one incubation chamber while sequentially adding, incubating and removing the sample and pre-stored buffers for extraction. As the recovery rate of the typically low concentration of cfDNA is of high importance to attain sufficient amounts for analysis, optimal beadhandling is paramount. The goal is that the cfDNA in the sample adsorbs to the solid phase completely during the binding step, is retained during washing and completely removed during elution. In this work, we improved beadhandling by optimizing the incubation chamber geometry and both frequency and temperature protocols, to maximize recovery rates. For characterization of the extraction performance, synthetic mutant DNA was spiked into human plasma samples. The LabDisk showed better reproducibility in DNA recovery rates with a standard deviation of ±13% compared to a manual approach using spin-columns (±17%) or nanobeads (±26%). The extraction of colorectal cancer samples with both the developed LabDisk and a robotic automation instrument resulted in comparable allele frequencies. Consequently, we present a highly attractive solution for an automated liquid biopsy cfDNA extraction in a small benchtop device.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...