Concurrently enhanced dielectric properties and energy density in poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based core–shell BaTiO3 nanocomposites via constructing a polar and rigid polymer interfacial layer†
Abstract
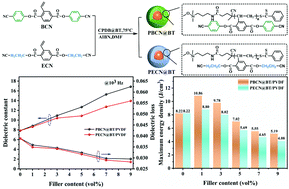
The interfacial zone plays a key role in regulating the dielectric capabilities of polymer-based composites. In this article, two kinds of polar polymers were designed and selected as the shell layer of BaTiO3 nanoparticles to investigate the influence of the chain conformation and band-gap width of an interfacial modifier on the dielectric behavior and energy storage properties of ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)-based nanocomposites. Compared with the polar coil-chain cyano-polymer poly[bis(2-cyanoethyl)-2-vinylterephthalate] (PECN), the polar rigid-chain cyano-polymer poly[bis(4-cyanophenyl)-2-vinylterephthalate] (PBCN) modifier with a high dielectric constant (εr) and low band-gap width showed a more noticeable effect on the enhanced dielectric and energy density storage of PVDF-based nanocomposites. The εr of PBCN@BT/PVDF nanocomposites increased from 7.8 to 16.9 at 103 Hz with the increasing PBCN@BT content from 0 vol% to 9 vol%. In addition, the highest breakdown strength of 464 MV m−1 and the maximum discharge energy density of 10.86 J cm−3 were achieved in 1 vol%-PBCN@BT/PVDF nanocomposites due to the higher electron affinity. This work furnishes a potential pathway for reaching the high-energy-density of polymer-based nanocomposites by taking the rigid polymer modifier with a low band-gap width.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...