Inherent characteristics of ultra-photosensitive Al/Cu–CeO2/p-Si metal oxide semiconductor diodes
Abstract
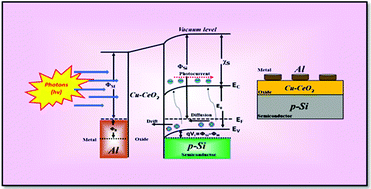
An ultrahigh photosensitive diode was developed using a Cu-doped CeO2 thin film through spray pyrolysis processing, which has made a unique contribution in the field of optoelectronic device fabrication process. Phase identification revealed a good arrangement of atoms in the as-prepared nanostructured thin films via structural analysis. The formation of wire-shaped nanorods was confirmed. Elemental distribution and their valence states were systematically monitored using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis, where the presence of Ce3+ was evidenced. Good mechanical properties were obtained owing to the Cu-doping in the cerium host matrix, which was investigated by nano-indentation. Bandgap energy fluctuation was the root cause for electrical conductivity. The present work revealed a decrease in the band gap energy upon Cu-doping alters the electrical conductivity. An as-fabricated photodiode demonstrated superior detectability upon Cu-doping. In the depletion region, on account of a high surface-to-volume ratio, the generation of electron–hole pairs increased along with photoresponsivity with increases in the quantum efficiency and current gain.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...