Nickel cobaltite/multi-walled carbon nanotube flexible sensor for the electrochemical detection of dopamine released by human neural cells†
Abstract
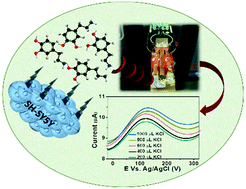
The importance of dopamine as a biomarker in both physiological and social domains has piqued scientist's interest. The development of miniaturized electrochemical devices capable of delivering a timely output on demand is a top priority in biomedical research. Herein, we attempted to fabricate an all-integrated flexible sensor for the cost-effective detection of dopamine. As a first step, we present a readily synthesizable nickel cobaltite/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite for dopamine sensing with a limit of detection of 60 nM even in the presence of a large number of interfering species. The utility of the composite sensor was demonstrated by its ability to detect dopamine released by human SH-SY5Y neuronal cell culture. The detection of dopamine in real-life samples such as artificial sweat and human serum with detection limits of 65 nM and 68 nM, respectively, demonstrated the developed sensor's excellent sensitivity. As a result, the nickel cobaltite/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite-based all-integrated flexible sensor was fabricated for detecting dopamine at a concentration of 1 nM. The all-integrated flexible sensor was assembled as a proof-of-concept to directly detect dopamine released by human neural cells. Further, the mechanism of the interaction between dopamine, nickel cobaltite, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes was revealed from adsorption energy calculations using Density Functional Theory (DFT).
- This article is part of the themed collections: #RSCPoster Conference and Celebrating International Women’s Day: Women in Materials Science


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...