A cationic BODIPY photosensitizer decorated with quaternary ammonium for high-efficiency photodynamic inhibition of bacterial growth†
Abstract
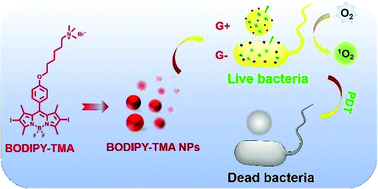
On account of the constant evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, the effects of existing antibacterial materials are being gradually weakened, and the difficulty in curing infectious diseases is increasing. Therefore, more novel antibacterial materials or methods are eagerly required to combat microbial infections. Recently, the advantages of photodynamic therapy in the antibacterial field have gradually been validated. Herein, a trimethylamine (TMA) salt-modified 4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene (BODIPY) photosensitizer (BODIPY–TMA) was synthesized for antibacterial applications. Due to the positive charge of the TMA group, enhanced interactions were observed between the prepared BODIPY–TMA nanoparticles (BODIPY–TMA NPs) and negatively-charged bacterial membranes. The BODIPY–TMA NPs showed much better antibacterial effect toward both S. aureus and E. coli compared with their BODIPY–Br NPs counterpart without a positive charge. Moreover, the BODIPY–TMA NPs efficiently prevented the formation of biofilms and destroyed pre-established biofilms. Thus, such positively-charged photosensitizers may pave the way for the exploration of highly effective antibacterial agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...