Effective topical treatments using innovative NNO-tridentate vanadium(iv) complexes-mediated photodynamic therapy in a psoriasis-like mouse model†
Abstract
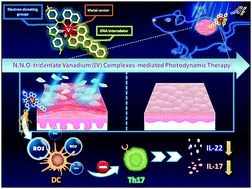
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that can significantly impact the quality of human life. Various drug treatments are available; however, due to their long-term severe side effects the usage of these drugs is limited. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been clinically approved for skin diseases due to its non-invasive nature. We present novel NNO-tridentate vanadium(IV) complexes used in PDT for anti-inflammatory effects in an imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin disease mouse model. The vanadium(IV) complexes (1–4) were synthesized using the NNO-tridentate ligand with a benzo[i]dipyrido[3,2-a;2′,3′-c]phenazine (dppn) moiety, and were characterized by UV/Visible spectroscopy, EPR spectroscopy, NMR (1H, and 13C) spectroscopy, electrospray ionization mass (ESI-MS) spectrometry and cyclic voltammetry (CV) studies. The photocytotoxicity of vanadium(IV) complexes (1–4) was low under dark conditions and complex (4) showed remarkable photocytotoxicity under blue light (430 nm, 8 W cm−2, 30 min) irradiation. Moreover, [VO(t-butylL)(dppn)] (4)-mediated PDT down-regulated inflammatory cytokines IL-17A and IL-22 in the psoriasis-like mouse model, which could evidence the significant relieving of the psoriatic-like symptoms in the mouse model. Overall, these results suggested that [VO(t-butylL)(dppn)] (4) could be a potential candidate for the treatment of psoriasis both in vitro and in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...