Amphiphilic shell nanomagnetic adsorbents for selective and highly efficient capture of low-density lipoprotein from hyperlipidaemia serum†
Abstract
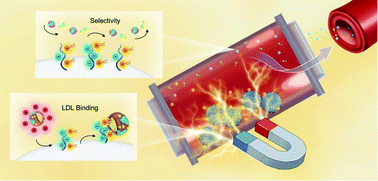
Removal of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from hyperlipemia patients’ blood represents an effective approach to prevent the progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Based on the LDL structural characteristics and intermolecular interactions, a tailored nano-adsorbent (Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-PE) was prepared aimed at the removal of LDL from hyperlipemia serum with high selectivity. The core–shell structured magnetic nanoparticles were embedded in an amphiphilic layer composed of hydrophilic poly(acrylic acid) and lipophilic phospholipids to provide multifunctional binding for LDL particles. The results of dynamic light scattering, water contact angle and zeta-potential measurements, thermal gravimetric analysis, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy together with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirmed the core–shell structured nanoparticles bearing amphiphilic poly acrylic acid and phospholipid molecules. Because of the superior electronegativity of the functional layer, the nano-adsorbent demonstrated favorable adsorption selectivity against high-density lipoprotein, which possesses a similar structure to LDL but has a cardio-protective function in the human body. The respective adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-PE towards LDL, total cholesterol and triglycerides reached up to 6.26 mg g−1, 8.41 mg g−1 and 9.19 mg g−1, which was 7.03, 9.45 and 10.32 times that towards HDL (0.89 mg g−1). The kinetic and isothermal studies revealed that multiple interactions containing both physical and chemical adsorption occurred in the binding procedure between LDL and Fe3O4@SiO2@PAA-PE, and chemical adsorption may play a more predominant role in LDL adsorption. The nano-adsorbent also had negligible effects on blood cells, and possessed satisfactory recyclability, low cytotoxicity and hemolysis ratios, indicating its good application prospects as a hemoperfusion adsorbent in the treatment of hyperlipidaemia.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...