Facile fabrication of biodegradable endothelium-mimicking coatings on bioabsorbable zinc-alloy stents by one-step electrophoretic deposition†
Abstract
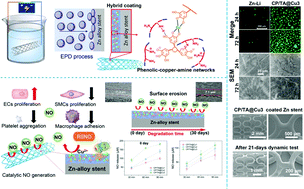
The zinc-alloy stent is one of the best potential candidates for bioabsorbable metal stents because of its appropriate corrosion rate aligned to the duration of the healing process of the surrounding vessel tissues. However, excessive release of zinc ions, causing cytotoxicity of endothelial cells, and insufficient surface bio-functions of Zn-alloy stents lead to considerable challenge in their application. Herein, one-step electrophoretic deposition was employed to apply a hybrid coating of polycarbonate, tannic acid, and copper ions with tailored functions on Zn-alloy stents to enhance their corrosion resistance and provide an endothelium-mimicking surface. Specifically, the synthesized amino-functionalized aliphatic polycarbonates endowed the hybrid coating with specific surface-erosion properties, resulting in superior corrosion resistance and long-term stability in degradation tests both in vitro and in vivo. The immobilized copper ions enabled the catalytic generation of nitric oxide and promoted the adhesion and proliferation of endothelial cells on zinc alloy. The added tannic acid firmly chelated the copper ions and formed durable phenolic-copper-amine crosslinked networks by electrostatic interaction, resulting in long-term stability of the hybrid coating during the 21 day dynamic immersion test. Tannic acid exerted a synergistic antibacterial effect with copper ions as well as a reduction in the inflammatory response to the zinc substrate. In addition, the hybrid coating improved the in vitro hemocompatibility of zinc alloys. By adjusting the amount of chelated copper in the coating system, the biological function of the corresponding coatings can be controlled, providing a facile surface treatment strategy to promote the progress of zinc-alloy stents in clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...