Microfluidics-assisted synthesis and functionalization of monodisperse colloidal hydrogel particles for optomechanical biosensors†
Abstract
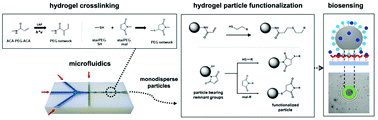
The soft colloidal probe (SCP) assay is a highly versatile sensing principle employing micrometer-sized hydrogel particles as optomechanical transducer elements. We report the synthesis, optimization, and conjugation of SCPs with defined narrow size distribution and specifically tailored mechanical properties and functionalities for integration into a microinterferometric optomechanical biosensor platform. Droplet-based microfluidics was used to crosslink polyethylene glycol (PEG) macromonomers by photocrosslinking and thiol-Michael addition. The effect of several synthesis parameters, i.e. PEG and radical initiator solid content, molecular weight and architecture of macromonomers, as well as UV exposure time and energy, were examined. SCPs were characterized with regard to the conversion of contained functional groups, morphology and mechanical properties by bright-field, confocal laser scanning and reflection interference contrast microscopy, as well as force spectroscopy. Functional groups were introduced during SCP synthesis and by several post-synthesis procedures, based on photoradical grafting and thiol-Michael addition. Preparation of SCPs by thiol-Michael addition and subsequent coupling of maleimide derivatives to unreacted thiols proved to be the superior strategy, while other approaches were associated with changes in the properties of the SCP. The newly developed SCPs were tested for their sensing capabilities employing the biotin–streptavidin-system. Biotin detection in the range of 10−7 to 10−10 M verified the concept of the synthesis strategy and the advantage of using monodisperse SCPs for easier and faster sensing applications of the SCP assay.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...