Dual-imaging magnetic nanocatalysis based on Fenton-like reaction for tumor therapy†
Abstract
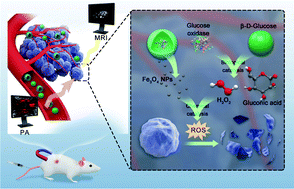
Sequential nano-catalytic therapy has emerged as a novel therapeutic modality for cancer treatment as it utilizes the unique tumor microenvironment for selective tumor treatment. This study reports a magnetic nanoparticle to achieve Fenton-like reaction and dual-imaging guidance/monitoring. Natural glucose oxidase (GOx) and superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles have been integrated into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) to fabricate a sequential nanocatalyst (designated as GOx@PLGA-Fe3O4). This nanocatalyst can functionally deplete glucose in tumor tissues, producing a considerable amount of highly cytotoxic hydroxyl radicals via the sequential Fenton-like reaction, and meanwhile maximizing the potential imaging capability as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging and photoacoustic imaging. By ribonucleic acid sequencing (RNA-seq) technology, GOx@PLGA-Fe3O4 nanoparticles are demonstrated to induce tumor cell death by inhibiting multiple gene regulation pathways involving tumor growth and recurrence. Therefore, this finding provides a novel strategy to achieve promising therapeutic efficacy by the rational design of multifunctional nanoparticles with various features, including magnetic targeting, sequential nano-catalytic therapy, and dual-imaging guidance/monitoring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...