Co-sputtering of lithium vanadium oxide thin films with variable lithium content to enable advanced solid-state batteries†
Abstract
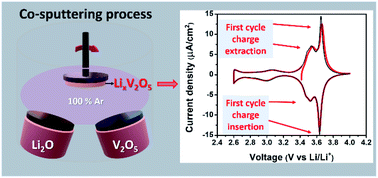
Advanced solid-state batteries most likely will entail aggressive structures or architectures with constraints that typically limit processing temperatures. Considering this, we have identified the importance of providing lithiated electrode materials at a modest processing temperature. Here we describe a pathway to meet this by the development of a co-sputtering process using lithium oxide and vanadium oxide targets which enables the growth of lithiated vanadium oxide (LVO) thin films for application in solid-state batteries. Analysis of the structure and film composition of samples deposited with different co-sputtering rate ratios and post-annealing shows that multiple phases of LixV2O5 likely coexist (i.e. α-, ε-, δ-, and γ-V2O5), and that this is unchanged after electrochemical cycling. The co-sputtering process can tune the lithium content up to a highly lithiated state of at least Li2V2O5. Electrochemical half-cells showed a significant amount of lithium available on the first charge (delithiation of LVO). LVO samples post-annealed at 300 °C showed typical redox peaks for LixV2O5 for both one and two lithium insertion reactions, which were highly reversible in most cases. A thin-film solid-state battery prototype using LVO as a cathode had 20% of the expected capacity, although the coulombic efficiency is near 100% at a fast rate (22C). This co-sputtering technique represents an opportunity for low temperature synthesis of pre-lithiated cathodes for thin film batteries, and introduces a broader methodology of depositing metal oxides with different alkali metal contents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...