Intermetallic Cu11In9in situ formed on hierarchical nanoporous Cu for highly selective CO2 electroreduction†
Abstract
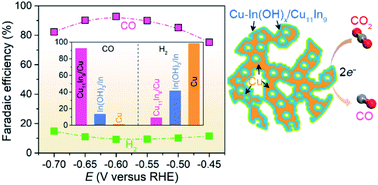
Developing highly selective and cost-effective electrocatalysts is crucial for the efficient conversion of CO2 to value-added carbon products. Here, we report intermetallic Cu11In9 nanoparticles that are in situ formed on nanoporous Cu skeleton (Cu11In9/Cu) as highly selective and electroactive catalysts to mediate CO2 electroreduction to CO. Owing to the high oxophilicity of surface indium atoms, their spontaneous hydroxylation results in the formation of heterogeneous Cu–In(OH)x surface on monoclinic Cu11In9 nanoparticles, which selectively boosts reaction kinetics of CO2-to-CO conversion as a result of weakening adsorption energies of *CO and H* intermediates on surface Cu atoms. Associated with hierarchical nanoporous Cu architecture to offer a high specific surface area for full use of electroactive sites and facilitate electron and mass transports along interconnective Cu ligaments and interpenetrative nanopores, nanoporous Cu11In9/Cu hybrid electrodes exhibit exceptional electrocatalysis for CO product, with a high partial current density of 12.6 mA cmgeo−2 and high faradaic efficiency of 92.8%, as well as excellent stability for more than 240 h at an overpotential of 0.49 V. These outstanding electrochemical properties make them attractive alternatives to precious Au- and Ag-based electrocatalysts for high-performance CO2 electrolysers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...