Redispersion strategy for high-loading carbon-supported metal catalysts with controlled nuclearity†
Abstract
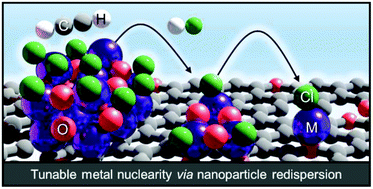
Supported low-nuclearity metal catalysts integrating single atoms or small clusters have emerged as promising materials for diverse applications. While sophisticated synthetic methods provide a high level of nuclearity control in the subnanometre regime, these routes do not fulfil the requirements for translation into industrial practice of (i) effectiveness for high metal contents and (ii) facile scalability. Herein, we present a gas-phase redispersion strategy consisting of sequential C2H2 and HCl treatments to gradually disperse Ru, Rh and Ir nanoparticles supported on commercial activated carbon with metal content up to 10 wt% and initial average sizes of ≈ 1 nm into small clusters and eventually single atoms. Avoidance of nanoparticle surface overchlorination, which hinders C2H2 adsorption, is identified as key for the redispersion process, as demonstrated by the inefficacy of both C2H2–HCl cofeeding and inverse sequence (i.e., HCl first) treatments. Precise size control (±0.1 nm) is enabled by regulating the number of C2H2–HCl cycles. Detailed characterisation by X-ray absorption spectroscopy, electron paramagnetic resonance and time-resolved mass spectrometry reveals that the redispersion occurs via a layer-by-layer mechanism. Specifically, the migration of surface chlorinated metal species to the carbon support is induced by the C2H2 treatment, depleting accessible surface Cl atoms, while the subsequent HCl treatment rechlorinates the cluster surface. The strategy paves the way for the generation of high-density metal sites with tuneable nuclearity for tailored applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Single-Atom Catalysis


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...