Adsorption of sterically-stabilized diblock copolymer nanoparticles at the oil–water interface: effect of charged end-groups on interfacial rheology†
Abstract
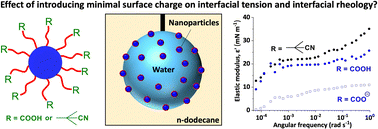
The RAFT aqueous emulsion polymerization of either methyl methacrylate (MMA) or benzyl methacrylate (BzMA) is conducted at 70 °C using poly(glycerol monomethacrylate) (PGMA) as a water-soluble precursor to produce sterically-stabilized diblock copolymer nanoparticles of approximately 30 nm diameter. Carboxylic acid- or morpholine-functional RAFT agents are employed to confer anionic or cationic functionality at the ends of the PGMA stabilizer chains, with a neutral RAFT agent being used as a control. Thus the electrophoretic footprint of such minimally-charged model nanoparticles can be adjusted simply by varying the solution pH. Giant (mm-sized) aqueous droplets containing such nanoparticles are then grown within a continuous phase of n-dodecane and a series of interfacial rheology measurements are conducted. The interfacial tension between the aqueous phase and n-dodecane is strongly dependent on the charge of the terminal group on the stabilizer chains. More specifically, neutral nanoparticles produce a significantly lower interfacial tension than either cationic or anionic nanoparticles. Moreover, adsorption of neutral nanoparticles at the n-dodecane–water interface produces higher interfacial elastic moduli than that observed for charged nanoparticles. This is because neutral nanoparticles can adsorb at much higher surface packing densities owing to the absence of electrostatic repulsive forces in this case.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...