Single cell force spectroscopy of erythrocytes at physiological and febrile temperatures reveals mechano-modulatory effects of atorvastatin
Abstract
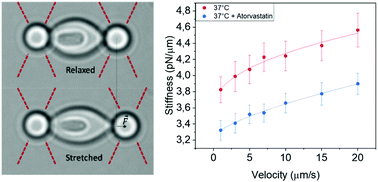
RBCs are mechanically active cells and constantly deform as they circulate through vasculature. Their mechanical properties can be significantly altered by various pathophysiological conditions, and the alterations in RBC mechanics can, in turn, have functional consequences. Although numerous mechanical studies have been conducted on RBCs, surprisingly, strain-rate and temperature dependent mechanics of RBCs have not been systematically examined, and current data is primarily based on measurements at room temperature. Here, we have used state-of-the-art single-cell optical tweezers to probe atorvastatin-induced changes of RBC mechanics and its strain-rate dependency at physiologically and medically relevant temperatures. Our data indicate that RBC mechanics is strain-rate and temperature dependent, and atorvastatin treatment softens RBCs at physiological temperature, but not at febrile temperature. The observed mechanical change is a notable side effect of the drug in some therapeutic applications. However, the mechano-modulatory effects of atorvastatin on erythrocytes at physiological temperature might offer new therapeutic possibilities for diseases related to blood cell mechanics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...