Structures of cationic and anionic polyelectrolytes in aqueous solutions: the sign effect†
Abstract
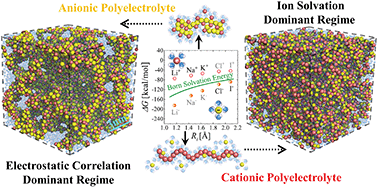
In this study, we use molecular dynamics simulation to explore the structures of anionic and cationic polyelectrolytes in aqueous solutions. We first confirm the significantly stronger solvation effects of single anions compared to cations in water at the fixed ion radii, due to the reversal orientations of asymmetric dipolar H2O molecules around the ions. Based on this, we demonstrate that the solvation discrepancy of cations/anions and electrostatic correlations of ionic species can synergistically cause the nontrivial structural difference between single anionic and cationic polyelectrolytes. The cationic polyelectrolyte shows an extended structure whereas the anionic polyelectrolyte exhibits a collapsed structure, and their structural differences decline with increasing the counterion size. Furthermore, we corroborate that multiple cationic polyelectrolytes or multiple anionic polyelectrolytes can exhibit largely differential molecular architectures in aqueous solutions. In the solvation dominant regime, the polyelectrolyte solutions exhibit uniform structures; whereas, in the electrostatic correlation dominant regime, the polyelectrolyte solutions exhibit heterogeneous structures, in which the likely charged chains microscopically aggregate through counterion condensations. Increasing the intrinsic chain rigidity causes polyelectrolyte extension and hence moderately weakens the inter-chain clustering. Our work highlights the various, unique structures and molecular architectures of polyelectrolytes in solutions caused by the multi-body correlations between polyelectrolytes, counterions and asymmetric dipolar solvent molecules, which provides insights into the fundamental understanding of ion-containing polymers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...