Measurements of interactions between fluorescent molecules and polyethylene glycol self-assembled monolayers
Abstract
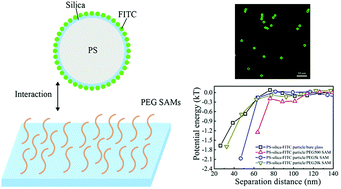
Blocking the non-specific binding of fluorescent biomolecules to substrates is one of the most important approaches to minimize the background noise in single-molecule fluorescence detection. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and its derivatives are the most frequently used self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) for surface passivation because they are particularly effective to reduce the adsorption of a majority of biomolecules. Most studies related to PEG SAMs focus only on the interactions between biomolecules and substrates, while few reports exist in which the interactions between fluorophores and organosilane SAMs are directly examined. The objective of this study is to try to clarify the interactions between fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and PEG SAMs at different ionic strengths. Total internal reflection microscopy (TIRM) was utilized for quantitative analysis of the interactions. At low ionic strength, long-range attractions between FITC-modified polystyrene–silica particles and PEG SAM grafting substrates were observed, even though both of them had an ensemble-averaged negative charge. The origin of this attraction could be correlated to their nonuniformly charged surfaces. At high ionic strength, van der Waals attraction at short distances was measured as the electrostatic interactions were completely screened. Due to the polarizability of the FITC molecule, the van der Waals attractions increased with the thickness of the PEG SAMs. This phenomenon is explained by the hydration shell of the PEG SAMs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...