Core–shell-structured and hydrogen-evolution-suppressing zinc anode for high stability Zn–Ni secondary batteries†
Abstract
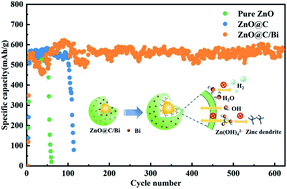
Bismuth-anchored carbon-coated ZnO (ZnO@C/Bi) with a unique core–shell structure was successfully prepared by a two-step solvothermal method and a subsequent calcination process. ZnO@C/Bi presents a structure characteristic that has ZnO as the core and high hydrogen evolution overpotential bismuth element-anchored porous amorphous carbon as the shell. Compared with pure ZnO, ZnO@C/Bi shows excellent cycling performance with a higher specific discharge capacity of 573.5 mA h g−1 after 620 cycles at 1C when the ZnO@C/Bi materials were applied as anode active substances in zinc–nickel (Zn–Ni) secondary batteries. The excellent electrochemical performance of ZnO@C/Bi could be attributed to the unique shell, which can not only effectively inhibit dendrite growth on the zinc anode but can also improve the hydrogen evolution overpotential with bismuth anchoring to inhibit the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of the zinc anode. This work provides a theoretical basis for designing zinc anodes with a core–shell structure and unveiling the prospects of ZnO restricted area materials for ultra-stable anodes. In addition, the unique core–shell structure may provide new insights into the anodes of alkali metal ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...