Highly sensitive urine glucose detection with graphene field-effect transistors functionalized with electropolymerized nanofilms†
Abstract
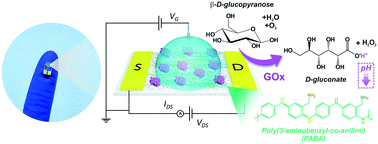
We introduce a new approach for glucose oxidase (GOx) immobilization on graphene field-effect transistors (gFETs) to fabricate highly sensitive glucose sensors. The strategy relies on the electropolymerization of a layer of the copolymer poly(3-amino-benzylamine-co-aniline) (PABA) on graphene-based transistors. The synthesized polymer film provides the suitable electrostatic charge and non-denaturing environment for enzyme immobilization without the need of any chemical primer. Then, the local pH changes triggered by the enzyme-catalyzed oxidation produce a shift in the Dirac potential of the gFETs to more negative values, which is evidenced by the differences in the graphene channel conductivity and constitutes the signal transduction mechanism of the sensing devices. The assembled biosensors revealed a low LOD of 4.1 μM and were capable of detecting glucose in the range from 10 to 1000 μM in a flow configuration. Moreover, they showed sensitivity of −24.9 μA per decade of glucose concentration and a fast response time, with an average value of 190 seconds, while allowing the operation at small gate-source and drain-source voltages. Finally, the biosensors were able to successfully monitor the analyte in urine samples, showing their potential towards the fabrication of point-of-care glucose testing devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Latin American Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...