Biomimetic catalytic aerobic oxidation of C–sp(3)–H bonds under mild conditions using galactose oxidase model compound CuIIL†
Abstract
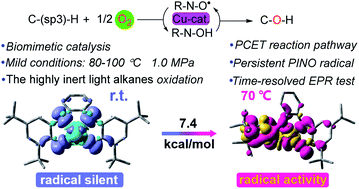
Developing highly efficient catalytic protocols for C–sp(3)–H bond aerobic oxidation under mild conditions is a long-desired goal of chemists. Inspired by nature, a biomimetic approach for the aerobic oxidation of C–sp(3)–H by galactose oxidase model compound CuIIL and NHPI (N-hydroxyphthalimide) was developed. The CuIIL–NHPI system exhibited excellent performance in the oxidation of C–sp(3)–H bonds to ketones, especially for light alkanes. The biomimetic catalytic protocol had a broad substrate scope. Mechanistic studies revealed that the CuI-radical intermediate species generated from the intramolecular redox process of CuIILH2 was critical for O2 activation. Kinetic experiments showed that the activation of NHPI was the rate-determining step. Furthermore, activation of NHPI in the CuIIL–NHPI system was demonstrated by time-resolved EPR results. The persistent PINO (phthalimide-N-oxyl) radical mechanism for the aerobic oxidation of C–sp(3)–H bond was demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...