Perpetuating enzymatically induced spatiotemporal pH and catalytic heterogeneity of a hydrogel by nanoparticles†
Abstract
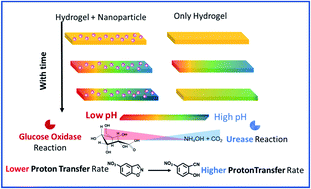
The attainment of spatiotemporally inhomogeneous chemical and physical properties within a system is gaining attention across disciplines due to the resemblance to environmental and biological heterogeneity. Notably, the origin of natural pH gradients and how they have been incorporated in cellular systems is one of the most important questions in understanding the prebiotic origin of life. Herein, we have demonstrated a spatiotemporal pH gradient formation pattern on a hydrogel surface by employing two different enzymatic reactions, namely, the reactions of glucose oxidase (pH decreasing) and urease (pH increasing). We found here a generic pattern of spatiotemporal change in pH and proton transfer catalytic activity that was completely altered in a cationic gold nanoparticle containing hydrogel. In the absence of nanoparticles, the gradually generated macroscopic pH gradient slowly diminished with time, whereas the presence of nanoparticles helped to perpetuate the generated gradient effect. This behavior is due to the differential responsiveness of the interface of the cationic nanoparticle in temporally changing surroundings with increasing or decreasing pH or ionic contents. Moreover, the catalytic proton transfer ability of the nanoparticle showed a concerted kinetic response following the spatiotemporal pH dynamics in the gel matrix. Notably, this nanoparticle-driven spatiotemporally resolved gel matrix will find applicability in the area of the membrane-free generation and control of spatially segregated chemistry at the macroscopic scale.
- This article is part of the themed collection: #RSCPoster Conference


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...