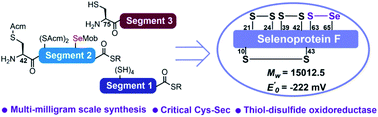
Chemical synthesis of human selenoprotein F and elucidation of its thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase activity†
Abstract
Selenoprotein F (SelF) is an endoplasmic reticulum-residing eukaryotic protein that contains a selenocysteine (Sec) residue. It has been suggested to be involved in a number of physiological processes by acting as a thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase, but the exact role has remained unclear due to the lack of a reliable production method. We document herein a robust synthesis of the human SelF through a three-segment two-ligation semisynthesis strategy. Highlighted in this synthetic route are the use of a mild desulfurization process to protect the side-chain of the Sec residue from being affected and the simultaneous removal of acetamidomethyl and p-methoxybenzyl protection groups by PdCl2, thus facilitating the synthesis of multi-milligrams of homogenous SelF. The reduction potential of SelF was determined and the thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase activity was further supported by its ability to catalyze the reduction and isomerization of disulfide bonds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...