Exciton interactions in helical crystals of a hydrogen-bonded eumelanin monomer†
Abstract
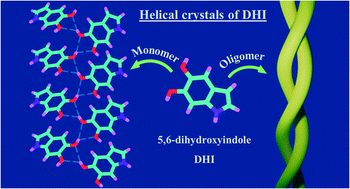
Eumelanin, a naturally occurring group of heterogeneous polymers/aggregates providing photoprotection to living organisms, consist of 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI) and 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) building blocks. Despite their prevalence in the animal world, the structure and therefore the mechanism behind the photoprotective broadband absorption and non-radiative decay of eumelanin remain largely unknown. As a small step towards solving the incessant mystery, DHI is crystallized in a non-protic solvent environment to obtain DHI crystals having a helical packing motif. The present approach reflects the solitary directional effect of hydrogen bonds between the DHI chromophores for generating the crystalline assembly and filters out any involvement of the surrounding solvent environment. The DHI single crystals having an atypical chiral packing motif (P212121 Sohncke space group) incorporate enantiomeric zig-zag helical stacks arranged in a herringbone fashion with respect to each other. Each of the zig-zag helical stacks originates from a bifurcated hydrogen bonding interaction between the hydroxyl substituents in adjacent DHI chromophores which act as the backbone structure for the helical assembly. Fragment-based excited state analysis performed on the DHI crystalline assembly demonstrates exciton delocalization along the DHI units that connect each enantiomeric helical stack while, within each stack, the excitons remain localized. Fascinatingly, over the time evolution for generation of single-crystals of the DHI-monomer, mesoscopic double-helical crystals are formed, possibly attributed to the presence of covalently connected DHI trimers in chloroform solution. The oligomeric DHI (in line with the chemical disorder model) along with the characteristic crystalline packing observed for DHI provides insights into the broadband absorption feature exhibited by the chromophore.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...