Fighting metallodrug resistance through alteration of drug metabolism and blockage of autophagic flux by mitochondria-targeting AIEgens†
Abstract
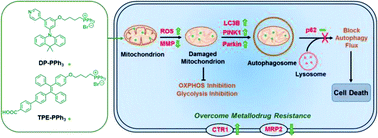
Metallodrug resistance has attracted a great deal of attention in cancer treatment. According to the cisplatin (cis-Pt) anticancer mechanism, a new strategy to overcome cis-Pt resistance through mitochondrial dysfunction is proposed. Two mitochondria-targeted aggregation-induced emission fluorogens (AIEgens) were first synthesized, named DP-PPh3 and TPE-PPh3, which showed superior capacities to overcome the cis-Pt resistance of lung cancer cells (A549R) by the alteration of drug metabolism (up-regulation of influx CTR1 and down-regulation of efflux MRP2) and blockage of autophagic flux (failure of the degradation of autophagosomes). This study is the first time that AIEgens are utilized in the treatment of cis-Pt resistant cancer cells. Moreover, the underlying molecular mechanism was fully revealed. Triphenylphosphonium (PPh3)-decorated AIEgens DP-PPh3 and TPE-PPh3 not only successfully realized aggregation and the imaging of mitochondria in A549R cells, but also activated cytotoxicity towards A549R cells. DP-PPh3 and TPE-PPh3 could induce ROS production, disrupt the mitochondrial structure, and impair mitochondrial and glycolytic metabolism. Furthermore, the anticancer efficacy of these drugs was demonstrated in 3D multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTSs) of A549R cells in vitro and in tumor-bearing nude mice in vivo. This AIE-PPh3 strategy not only promoted cytotoxicity towards cancer cells but also provided a new pathway for the treatment of metallodrug resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...