Concentration of stimulant regulates initial exocytotic molecular plasticity at single cells†
Abstract
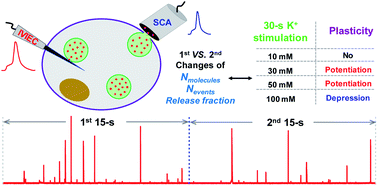
Activity-induced synaptic plasticity has been intensively studied, but is not yet well understood. We examined the temporal and concentration effects of exocytotic molecular plasticity during and immediately after chemical stimulation (30 s K+ stimulation) via single cell amperometry. Here the first and the second 15 s event periods from individual event traces were compared. Remarkably, we found that the amount of catecholamine release and release dynamics depend on the stimulant concentration. No changes were observed at 10 mM K+ stimulation, but changes observed at 30 and 50 mM (i.e., potentiation, increased number of molecules) were opposite to those at 100 mM (i.e., depression, decreased number of events), revealing changes in exocytotic plasticity based on the concentration of the stimulant solution. These results show that molecular changes initiating exocytotic plasticity can be regulated by the concentration strength of the stimulant solution. These different effects on early plasticity offer a possible link between stimulation intensity and synaptic (or adrenal) plasticity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...