A perfect match between borophene and aluminium in the AlB3 heterostructure with covalent Al–B bonds, multiple Dirac points and a high Fermi velocity†
Abstract
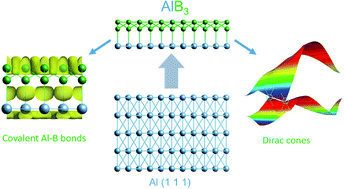
By performing a swarm-intelligent global structure search combined with first-principles calculations, a stable two-dimensional (2D) AlB3 heterostructure with directed, covalent Al–B bonds forms due to a nearly perfect lattice match between 2D borophene and the Al(111) surface. The AlB3 heterosheet with the P6mm space group is composed of a planar Al(111) layer and a corrugated borophene layer, where the in-plane coordinates of Al covalently link with the corrugated B atoms. The resulting structure shows a similar interlayer interaction energy to that of the Al(111) surface layer to the bulk and high mechanical and thermal stability, possesses multiple Dirac points in the Brillouin zone with a remarkably high Fermi velocity of 1.09 × 106 m s−1, which is comparable to that of graphene. Detailed analysis of the electronic structure employing the electron localisation function and topological analysis of the electron density confirm the covalent Al–B bond with high electron localisation between the Al and B centres and with only little interatomic charge transfer. The combination of borophene with metal monolayers in 2D heterostructures opens the door to a rich chemistry with potentially unprecedented properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...