Orally administered bismuth drug together with N-acetyl cysteine as a broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus cocktail therapy†
Abstract
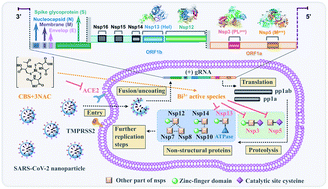
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern compromises vaccine efficacy and emphasizes the need for further development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics, in particular orally administered take-home therapies. Cocktail therapy has shown great promise in the treatment of viral infection. Herein, we reported the potent preclinical anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of a cocktail therapy consisting of clinically used drugs, e.g. colloidal bismuth subcitrate (CBS) or bismuth subsalicylate (BSS), and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). Oral administration of the cocktail reduced viral loads in the lung and ameliorated virus-induced pneumonia in a hamster infection model. The mechanistic studies showed that NAC prevented the hydrolysis of bismuth drugs at gastric pH via the formation of the stable component [Bi(NAC)3], and optimized the pharmacokinetics profile of CBS in vivo. Combination of bismuth drugs with NAC suppressed the replication of a panel of medically important coronaviruses including Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) and SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant (B.1.1.7) with broad-spectrum inhibitory activities towards key viral cysteine enzymes/proteases including papain-like protease (PLpro), main protease (Mpro), helicase (Hel) and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Importantly, our study offered a potential at-home treatment for combating SARS-CoV-2 and future coronavirus infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...