Highly effective removal of Hg(ii) solution using corn bract@MoS2 as a new biomass adsorbent†
Abstract
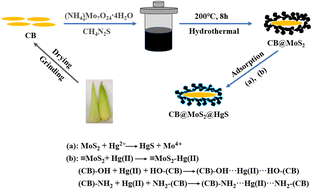
As known, mercury contamination is one of the current environmental issues due to the high toxicity of mercury. Corn bract (CB) is an agricultural by-product, and its final treatment is generally incineration that causes air pollution. In this study, a new type of high-efficiency biomass adsorbent (CB@MoS2) for adsorption of Hg(II) was obtained, and its morphology and structure were characterized with FT-IR, XRD, SEM and TEM. The results showed that when the pH value, Hg(II) ion concentration and adsorption time were 4, 100 mg L−1 and 120 min, the adsorption capacity and removal rate could reach 332.50 mg g−1 and 99.75%. In addition, CB@MoS2 had a good selectivity for Hg(II) ions. The adsorption behavior followed pseudo-second-order kinetics, indicating that the adsorption of Hg(II) ions by CB@MoS2 was a chemical adsorption. After five adsorption–desorption experiments, it still possessed good adsorption performance and effective regeneration. In short, CB@MoS2 has high efficiency and good reusability, and will become a candidate material for the treatment of mercury-containing industrial wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...