Synthesis of polyaspartic acid-capped 2-aminoethylamino acid as a green water treatment agent and study of its inhibition performance and mechanism for calcium scales†
Abstract
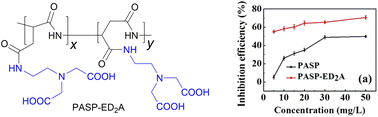
Polyaspartic acid (PASP), a well-known green scale inhibitor for industrial water treatment, might be decomposed with prolonged duration, and its anti-scaling performance against CaCO3 and CaSO4 is diminished at a low concentration (<10 mg L−1) and a high temperature. With semi-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) tetrasodium salt as the mimicking model, novel phosphorus-free PASP-capped 2-aminoethylamino acid (PASP–ED2A) containing side chains bearing multi-functional groups is rationally designed and successfully prepared via the ring-opening reaction of cheap poly(succinimide) under mild reaction conditions with the assistance of readily available 2-aminoethyl amino acid. The static scale inhibition method is used to evaluate the scale inhibition performance of the as-synthesized PASP derivative. Scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy are utilized to monitor the crystallization process of calcium carbonate and calcium sulfate scales, and density functional theory calculations are conducted to shed light on the relationship between the molecular structure and scale inhibition mechanism of PASP–ED2A. Results show that the as-prepared PASP–ED2A shows better scale inhibition performance for CaCO3 and CaSO4 than PASP with a low concentration, a high temperature, and an extended duration. Particularly, PASP–ED2A with a concentration of 10 mg L−1 exhibits the best scale inhibition performance for CaCO3; its scale inhibition capacity is about two times as much as that of PASP. The reason lies in that the coordination atoms in the molecular structure of PASP–ED2A can chelate with Ca2+ to inhibit the combination of Ca2+ with anions and prevent the generation of CaCO3 and CaSO4 scales. The PASP–ED2A derivative can more efficiently retard the formation and growth of CaCO3 and CaSO4 crystal nuclei and exerts better inhibition performance against CaCO3 and CaSO4 scales than PASP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...