Modification of silica nanoparticles by 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and 5-bromosalicylaldehyde as new nanocomposites for efficient removal and preconcentration of Cu(ii) and Cd(ii) ions from water, blood, and fish muscles
Abstract
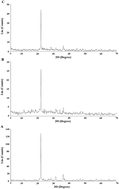
Herein, silica nanoparticles were modified by 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and 5-bromosalicylaldehyde to produce new nanocomposites which were abbreviated as N1 and N2, respectively. The synthesized nanocomposites were used for efficient removal and preconcentration of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions from water, blood, and fish muscles. FE-SEM, FT-IR, XRD, CHN elemental analysis, and nitrogen gas sorption analyzer were used to characterize the new nanocomposites. The XRD proved that the synthesized oxide is cristobalite with an average crystallite size of 54.80 nm. Due to the formation of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N group, the intensity of the XRD peak at 2θ = 21.9° in the N1 and N2 nanocomposites decreased significantly. The FT-IR bands, which appeared at 1603 and 1629 cm−1 in the N1 and N2 nanocomposites, are attributable to the bending vibration of C
N group, the intensity of the XRD peak at 2θ = 21.9° in the N1 and N2 nanocomposites decreased significantly. The FT-IR bands, which appeared at 1603 and 1629 cm−1 in the N1 and N2 nanocomposites, are attributable to the bending vibration of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N and/or OH, respectively. Also, the FE-SEM analysis shows the morphology of the silica nanoparticles which were identified as spherical and rod-like with slight agglomeration while the N1 and N2 nanocomposites have flaky surfaces due to the formation of C
N and/or OH, respectively. Also, the FE-SEM analysis shows the morphology of the silica nanoparticles which were identified as spherical and rod-like with slight agglomeration while the N1 and N2 nanocomposites have flaky surfaces due to the formation of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N groups. The maximum Cu(II) ion adsorption capacities of the N1 and N2 nanocomposites are 64.81 and 40.93 mg g−1, respectively. The maximum Cd(II) ion adsorption capacities of the N1 and N2 nanocomposites are 27.39 and 26.34 mg g−1, respectively. The adsorption of Cu(II) or Cd(II) ions using the synthesized nanocomposites is spontaneous, chemical, exothermic, and well-matched with the Langmuir equilibrium isotherm. The recovery findings demonstrate that the preconcentration process is accurate, adaptable, and resulted in quantitative separation because % Recovery is more than 95%. Furthermore, the % RSD was less than 3.5%, indicating good reproducibility.
N groups. The maximum Cu(II) ion adsorption capacities of the N1 and N2 nanocomposites are 64.81 and 40.93 mg g−1, respectively. The maximum Cd(II) ion adsorption capacities of the N1 and N2 nanocomposites are 27.39 and 26.34 mg g−1, respectively. The adsorption of Cu(II) or Cd(II) ions using the synthesized nanocomposites is spontaneous, chemical, exothermic, and well-matched with the Langmuir equilibrium isotherm. The recovery findings demonstrate that the preconcentration process is accurate, adaptable, and resulted in quantitative separation because % Recovery is more than 95%. Furthermore, the % RSD was less than 3.5%, indicating good reproducibility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...