Reductive removal of selenate (VI) in aqueous solution using rhodium metal particles supported on TiO2
Abstract
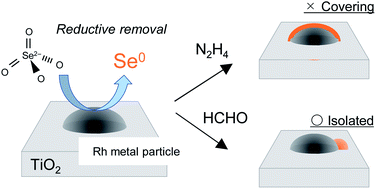
Selenium and its compounds in high concentration are toxic for humans, especially selenate (VI) is the most toxic due to its high solubility in water. To promote the reductive reaction of Se(VI) to Se(IV) or Se(0), which is relatively easy to remove in water, noble metal particles were added as reaction sites with a reductant. The highest removal performance of selenate in aqueous solution was achieved using rhodium particles supported on TiO2 (Rh/TiO2). Selenate was rapidly reduced with hydrazine on the metal particle, leading to a selenium deposition on the particle inhibiting the stable reductive reaction. On the other hand, when a weaker reductant such as formaldehyde was used for the selenate reduction, the selenium deposition was suppressed due to its low reactivity, resulting in a stable reductive reaction of selenate in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...