Adipogenesis or osteogenesis: destiny decision made by mechanical properties of biomaterials
Abstract
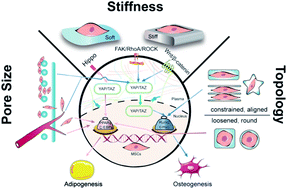
Regenerative medicine affords an effective approach for restoring defect-associated diseases, and biomaterials play a pivotal role as cell niches to support the cell behavior and decide the destiny of cell differentiation. Except for chemical inducers, mechanical properties such as stiffness, pore size and topography of biomaterials play a crucial role in the regulation of cell behaviors and functions. Stiffness may determine the adipogenesis or osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) via the translocation of yes-associated protein (YAP) and the transcriptional coactivator with a PDZ-binding motif (TAZ). External forces transmit through cytoskeleton reorientation to assist nuclear deformation and molecule transport, meanwhile, signal pathways including the Hippo, FAK/RhoA/ROCK, and Wnt/β-catenin have been evidenced to participate in the mechanotransduction. Different pore sizes not only tailor the scaffold stiffness but also conform to the requirements of cell migration and vessels in-growth. Topography guides cell geometry along with mobility and determines the cell fate ascribed to micro/nano-scale contact. Herein, we highlight the recent progress in exploring the regulation mechanism by the physical properties of biomaterials, which might lead to more innovative regenerative strategies for adipose or bone tissue repair.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...