Efficient conversion of lactic acid to alanine over noble metal supported on Ni@C catalysts†
Abstract
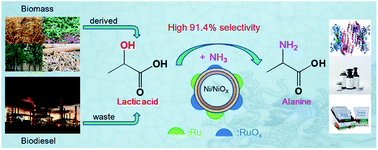
Alanine (Ala), regarded as the building block for protein synthesis, has been widely used in the field of food processing, pharmaceutical, and bio-based plastic industries. Containing plenty of oxygenic functional groups, biomass-derived chemicals are proper for Ala synthesis in an economic and green way via amination. In this work, lactic acid (LA) derived from renewable biomass and waste glycerol (the major by-product of biodiesel industry) was used to produce Ala. Here, a series of magnetic catalysts M/Ni@C (M = Ru, Pt, Pd, Ir, and Rh) were synthesized by ethylene glycol reduction of metal M supported on encapsulated Ni@C. Compared with catalysts based on other M metals, Ru/Ni@C catalysts exhibited extraordinary efficiency with 91.4% selectivity for Ala synthesis from LA (63.7% yield of Ala and 69.7% conversion of LA). The results of experiments and catalyst characterization indicated that the doping of M metals could improve the dehydrogenation ability of catalysts, as well as the ability of NH3 adsorption, facilitating the reaction towards Ala. Overall, this study provides an efficient chemo-catalytic way for the production of Ala from biomass-derived substrates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...