The hydroperoxyl antiradical activity of natural hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in physiological environments: the effects of pH values on rate constants†
Abstract
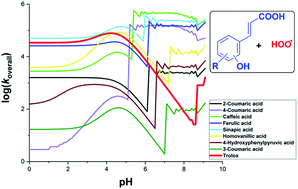
Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives (HCA) are a type of phenolic acid that occurs naturally. HCA are widely known for their anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and especially antioxidant capabilities; however, a comprehensive study of the mechanism and kinetics of the antiradical activity of these compounds has not been performed. Here, we report a study on the mechanisms and kinetics of hydroperoxyl radical scavenging activity of HCA by density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The ability of HCA to scavenge hydroperoxyl radicals in physiological environments was studied. The results showed that HCA had moderate and weak HOO˙ antiradical activity in pentyl ethanoate solvent, with the overall rate constant koverall = 8.60 × 101 − 3.40 × 104 M−1 s−1. The formal hydrogen transfer mechanism of phenyl hydroxyl groups defined this action. However, in water at physiological pH, 2-coumaric acid (1), 4-coumaric acid (2), caffeic acid (3), ferulic acid (4), sinapic acid (5) and 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (7) exhibit a significant HOO˙ antiradical activity with ktotal = 105 − 108 M−1 s−1 by the electron transfer reaction of the phenolate anions. Following a rise in pH levels in most of the studied substances, the overall rate constant varied. The acid 5 exhibited the highest HOO˙ radical scavenging activity (log(koverall) = 4.6–5.1) at pH < 5; however, at pH = 5.4–8.8, the highest HOO˙ radical scavenging activity were observed for 3 with log(koverall) = 5.2–5.7. At pH > 6.2, acids 2, 3, 4, and 5 presented the largest radical scavenging activity. By contrast, acid 3-coumaric acid (8) had the lowest antiradical activity at most pH values. Thus, the hydroperoxyl radical scavenging activity in pentyl ethanoate follows the order 3 > 5 > 1 ∼ 2 ∼ 4 ∼ 6 (homovanillic acid) ∼ 7 > 8, whereas it follows the order 3 > 2 ∼ 4 ∼ 5 > 6 ∼ 7 > 1 > 8 in water at pH = 7.40. The activity of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 are faster than those of the reference Trolox, suggesting that these HCA could be useful natural antioxidants in the aqueous physiological environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...