Rapid electrochemical quantification of trace Hg2+ using a hairpin DNA probe and quantum dot modified screen-printed gold electrodes†
Abstract
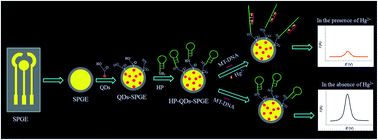
Rapid, simple, sensitive and specific approaches for mercury(II) (Hg2+) detection are essential for toxicology assessment, environmental protection, food analysis and human health. In this study, a ratiometric hairpin DNA probe based electrochemical biosensor, which relies on hairpin DNA probes conjugated with water-soluble and carboxyl functionalized quaternary Zn–Ag–In–S quantum dot (QD) on screen-printed gold electrodes (SPGE), referred to as the HP-QDs-SPGE electrochemical biosensor in this study, was developed for Hg2+ detection. Based on the “turn-off” reaction of a hairpin DNA probe binding with a mismatched target and Hg2+ through the formation of T–Hg2+–T coordination, the HP-QDs-SPGE electrochemical biosensor can rapidly quantify trace Hg2+ with high ultrasensitivity, specificity, repeatability and reproducibility. The conformational change of the hairpin DNA probe caused a significant decrease in electrochemical intensity, which could be used for the quantification of Hg2+. The linear dynamic range and high sensitivity of the HP-QDs-SPGE electrochemical biosensor for the detection of Hg2+ was studied in vitro, with a broad linear dynamic range of 10 pM to 1 μM and detection limits of 0.11 pM. In particular, this HP-QDs-SPGE electrochemical biosensor showed excellent selectivity toward Hg2+ ions in the presence of other metal ions. More importantly, this biosensor has been successfully used to detect Hg2+ in deionized water, tap water, groundwater and urine samples with good recovery rate and small relative standard deviations. In summary, the developed HP-QDs-SPGE electrochemical biosensor exhibited promising potential for further applications in on-site analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...