Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein entry using biologically modified polyacrylonitrile nanofibers: in vitro study towards specific antiviral masks†
Abstract
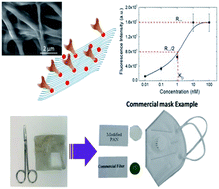
With the increase of the contagiousness rates of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), new strategies are needed to halt virus spread. Blocking virus entry by capturing its spike (S) protein is one of the effective approaches that could help in eliminating or reducing transmission rate of viruses. Herein, we aim to develop a nanofiber-based filter for protective face masks, composed of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers (NFs)-loaded with Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2) for capturing the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and blocking its entry. Docking simulations were performed to evaluate interactions of PAN with target proteins of both SARS-CoV-2 and Human Adenovirus type 5 (ADV-5) which was used as an in vitro model of human respiratory viruses. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transformed infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy was employed to investigate the surface morphology and to analyze the functional groups of the NFs, respectively. The mechanical properties of the electrospun NFs were investigated, according to which the tensile strengths of PAN and modified PAN NFs were 4.9 ± 1.2 GPa and 4.5 GPa. Additionally, elongations at break were 25 ± 2.5% to 24 ± 1.48% for PAN and modified PAN NFs. The tensile strength test showed good mechanical characteristics of the NFs. The ACE-2-loaded NFs were shown to be safe, with promising antiviral activity towards ADV-5. Meanwhile, a binding affinity study between the spike protein and ACE-2 was performed and the dissociation constant (KD) was found to be 1.1 nM. Accordingly, the developed antiviral filters have a potential role to stand as a base for combating various human respiratory viruses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...