Enhanced hydrogen storage properties of ZrTiVAl1−xFex high-entropy alloys by modifying the Fe content
Abstract
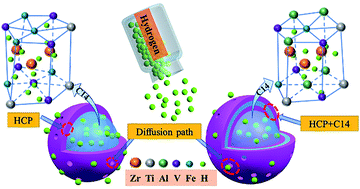
Lightweight ZrTiVAl high-entropy alloys have shown great potential as a hydrogen storage material due to their appreciable capacity, easy activation, and fast hydrogenation rates. In this study, transition metal Fe was used to improve the hydrogen storage properties of the equimolar ZrTiVAl alloy, and ZrTiVAl1−xFex (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1) alloys were prepared to investigate the microstructure evolution and hydrogen storage properties. The results show that the ZrTiVAl1−xFex alloys are composed of a C14 Laves phase and Ti-rich HCP phase. With Fe substituting Al, the fraction of the C14 Laves phase increases and that of the HCP phase decreases. Besides, the interdendritic area fraction reaches the maximum when the Fe ratio is 0.2. The element V transferred to the C14 Laves phase from the HCP phase, which is caused by the strong affinity between V and Fe. The ZrTiVAl1−xFex alloys show enhanced hydrogenation kinetics and capacities. Notably, the ZrTiVFe alloy can reversely absorb 1.58 wt% hydrogen even at room temperature under 1 MPa H2. The reduced interdendritic phase is beneficial to shorten the H atom diffusion distance, thus improving the hydrogenation rates. Both the transfer of the hydrogen-absorbing element V to the C14 Laves phase and the increased fraction of the C14 Laves phase lead to the increase of hydrogen storage capacity with the addition of Fe. Moreover, the increased Fe content leads to an increase of average valence electron concentration (VEC), where a larger VEC destabilizes the hydrides, and the desorption temperature of ZrTiVAl1−xFex hydride decreases significantly.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...