Curcumin assisted green synthesis of silver and zinc oxide nanostructures and their antibacterial activity against some clinical pathogenic multi-drug resistant bacteria
Abstract
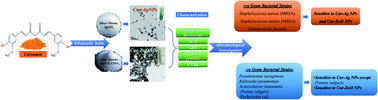
According to WHO warnings, the antibiotic resistance crisis is a severe health issue in the 21st century, attributed to the overuse and misuse of these medications. Consequently, the dramatic spreading rate of the drug-resistant microbial pathogens strains. The microbiological, biochemical tests and antibiotic sensitivity identified the bacteria's multi-drug resistance (MDR). About 150 different clinical samples were taken from hospitalized patients, both males, and females, ranging from 9 to 68 years. Gram-negative strains were (70.0%), while Gram-positive isolates were (30.0%). Among sixteen antibiotics, antibiotic susceptibility of imipenem was found to be the most efficient drug against most of the Gram-negative and Gram-positive isolates, followed by meropenem, depending on the culture and sensitivity results. All the experimental bacteria showed multidrug-resistant phenomena. In this study, green synthesized silver (Cur-Ag NPs) and zinc oxide (Cur-ZnO NPs) nanoparticles in the presence of curcumin extract. In addition, their physicochemical properties have been characterized using different techniques such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), and colloidal properties techniques. Furthermore, curcumin-capped silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) exhibited solid antimicrobial action against the experimental bacterial isolates, except Proteus vulgaris (i.e., P. vulgaris). Curcumin-capped zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) found antimicrobial activity against all tested strains. Finally, the minimum inhibitory concentration exhibited values from 3.9 to 15.6 μg ml−1, which is too small compared to other traditional antibiotics. In addition, the green-synthesized Cur-Ag NPs and Cur-ZnO NPs showed good biocompatibility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...