Thiazolidinedione derivatives as novel GPR120 agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes†
Abstract
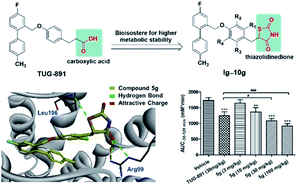
GPR120, also called FFAR4, is preferentially expressed in the intestines, and can be stimulated by long-chain free fatty acids to increase the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) from intestinal endocrine cells. It is known that GLP-1, as an incretin, can promote the insulin secretion from pancreatic cells in a glucose-dependent manner. Therefore, GPR120 is a potential drug target to treat type 2 diabetes. In this study, thiazolidinedione derivatives were found to be novel potent GPR120 agonists. Compound 5g, with excellent agonistic activity, selectivity, and metabolic stability, improved oral glucose tolerance in normal C57BL/6 mice in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, compound 5g exhibited anti-diabetic activity by promoting insulin secretion in diet-induced obese mice. In summary, compound 5g might be a promising drug candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...