Estimations of Fe0/−1–N2 interaction energies of iron(0)-dicarbene and its reduced analogue by EDA-NOCV analyses: crucial steps in dinitrogen activation under mild conditions†
Abstract
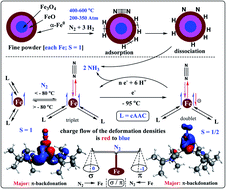
Metal complexes containing low valence iron atoms are often experimentally observed to bind with the dinitrogen (N2) molecule. This phenomenon has attracted the attention of industrialists, chemists and bio-chemists since these N2-bonded iron complexes can produce ammonia under suitable chemical or electrochemical conditions. The higher binding affinity of the Fe-atom towards N2 is a bit ‘mysterious’ compared to that of the other first row transition metal atoms. Fine powders of α-Fe0 are even part of industrial ammonia production (Haber–Bosch process) which operates at high temperature and high pressure. Herein, we report the EDA-NOCV analyses of the previously reported dinitrogen-bonded neutral molecular complex (cAACR)2Fe0–N2 (1) and mono-anionic complex (cAACR)2Fe−1–N2 (2) to give deeper insight of the Fe–N2 interacting orbitals and corresponding pairwise intrinsic interaction energies (cAACR = cyclic alkyl(amino) carbene; R = Dipp or Me). The Fe0 atom of 1 prefers to accept electron densities from N2 via σ-donation while the comparatively electron rich Fe−1 centre of 2 donates electron densities to N2 via π-backdonation. However, major stability due to the formation of an Fe–N2 bond arises due to Fe → N2 π-backdonation in both 1 and 2. The cAACR ligands act as a charge reservoir around the Fe centre. The electron densities drift away from cAAC ligands during the binding of N2 molecules mostly via π-backdonation. EDA-NOCV analysis suggests that N2 is a stronger π-acceptor rather than a σ-donor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...