Ultrasensitive flower-like TiO2/Ag substrate for SERS detection of pigments and melamine†
Abstract
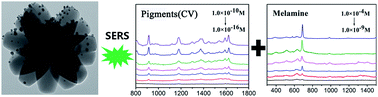
TiO2 flower like nanomaterials (FLNMs) are fabricated via a hydrothermal method and Ag nanoparticles (NPs) are deposited via electron beam evaporation. Several biological pigments (CV, R6G and RhB) are selected as target molecules to investigate their surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) property. The results demonstrate ultrasensitivity and high reproducibility. They reveal that the limit of detection (LOD) is 4.17 × 10−16 M and the enhancement factor (EF) is 2.87 × 1010 for CV, and the LOD is 5.01 × 10−16 M and 7.94 × 10−14 M for R6G and RhB, respectively. To assess the reproducibility on TiO2/Ag FLNMs SERS substrates, they are tested with 1.0 × 10−13 M of CV, 1.0 × 10−13 M of R6G and 1.0 × 10−11 M of RhB, respectively. The relative standard deviations (RSD) are less than 12.93%, 13.52% and 11.74% for CV, R6G and RhB, respectively. In addition, we carry out melamine detection and the LOD is up to 7.41 × 10−10 M, which is over 1000 times lower than the severest standards in the world. Therefore, the obtained TiO2 FLNMs have potential application in detecting illegal food additives.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...