Evaluation of the performance of different membrane materials for microalgae cultivation on attached biofilm reactors†
Abstract
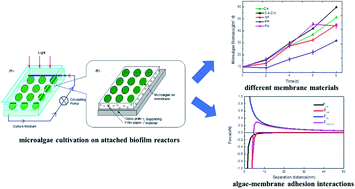
Attached microalgae production in wastewater is a promising method to further develop biofilm reactors by reducing economic costs associated with biomass separation and harvesting. However, the reliability of materials to support such adherence needs further investigation. Five common microfiltration membranes were evaluated in this study to assess their influence on the efficacy of harvesting Chlorella pyrenoidosa. The material-to-material, algae-to-algae, and algae-to-material interactions were studied based on the Extended Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, Overbeek (XDLVO) theory. The results showed that Chlorella pyrenoidosa was hydrophobic and that the algae particles derived from this algae type tended to agglomerate. Furthermore, the algae–membrane adhesion free energy further validated the accumulation of biomass in the experiments — the cellulose acetate nitrate (CACN) membrane and the cellulose acetate (CA) membrane obtained an optical biomass production of 59.93 and 51.27 g m−2. The presence of these interactions promoted the adhesion of more microalgae particles to the membrane. Moreover, the relationship between the algae–membrane and the distance at which the microalgae approached the membrane surface was simulated. The study indicated that the XDLVO theory could be successfully applied to the mechanism for the adhesion of the attached culture of Chlorella pyrenoidosa to the membrane material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...