Dual-targeting of the aromatase binding domain of heme and androstenedione by Pt(iv) prodrugs: a new treatment for postmenopausal breast cancer†
Abstract
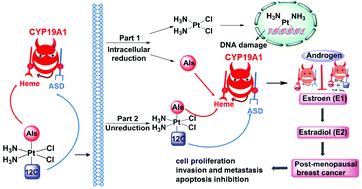
The combination of endocrine therapy and chemotherapy is an attractive approach for treating breast cancers. Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) are the first-line drugs for postmenopausal ER-positive breast cancer and adjuvant therapy drugs for early stages of breast cancer. In this paper, we employed the FDA-approved aromatase inhibitor aminoglutethimide (AG) to design and prepare a new class of multi-targeting Pt(IV) prodrugs (aminoplatins 1–3) by utilizing the targeting, estrogen-manipulating, and chemo-sensitizing effects of the aromatase inhibitor. Aminoplatin 3, as a representative, exhibited an enhanced anticancer activity up to 190-fold greater than the parent Pt(II) drug cisplatin, and 3 had less toxicity to normal cells, displaying higher anticancer efficacy and a superior therapeutic index compared to those of cisplatin. Moreover, aminoplatin 3 could enhance intracellular accumulation, induce remarkable DNA damage, inhibit migration and metastasis, and result in S phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ER-positive MCF-7 cells. Besides, molecular docking results showed that 3 simultaneously occupies the heme iron-binding domain and the ASD-binding site of aromatase by a highly efficient dual-binding pattern to aromatase, which further displayed a striking anti-estrogenic effect by significant downregulation of CPY19A1 and ERα in ER-positive MCF-7 cells. Most strikingly, our in vivo anticancer evaluation data also provided evidence that 3 effectively inhibited tumor growth and attenuated kidney toxicity compared to cisplatin in MCF-7 xenografted BALB/c nude mice. Our results suggest that the anticancer activity of aminoplatins is mechanistically distinct from that of the conventional platinum drugs, and modifying platinum drugs with aromatase inhibitors may represent an improved modality for the treatment of advanced postmenopausal breast cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...