Glutathione-triggered biodegradable poly(disulfide)s: ring-opening copolymerization and potent antibacterial activity†
Abstract
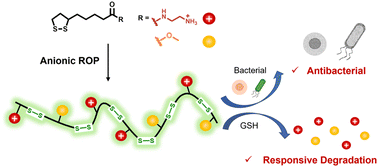
To combat multidrug-resistant bacteria, cationic amphiphilic polymers as mimics of host defense peptides have been designed and they demonstrated potent antibacterial activity. So far, most antibacterial polymers lack the ability to undergo responsive degradation. These chemically stable polymers may accumulate in the human body or in the environment, leading to cytotoxicity or inducing the evolution of antimicrobial resistance. Herein, we present the ring-opening polymerization of amino-functionalized lipoic acids that generate glutathione-triggered biodegradable poly(disulfide)s with potent antibacterial activity. The molecular weight and balance of cationic-and-hydrophobic properties of the poly(disulfide)s are systematically tuned to maximize the selective bactericidal ability over human cells. The optimal polymer kills both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens, including S. aureus and E. coli, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 100 μg mL−1. Meanwhile, the antibacterial activity of poly(disulfide)s can be turned off by glutathione-triggered degradation. Collectively, these poly(disulfide)s provide a molecular platform to develop antimicrobial agents that can fight multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, while avoiding their build-up in the body or environment, therefore decreasing the risk of adverse effects and bacterial resistance evolution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...