Synthesis of degradable double network gels using a hydrolysable cross-linker†
Abstract
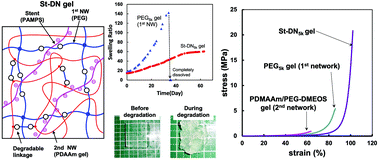
Double network (DN) gels have remarkably high mechanical strength and toughness and can be potentially applied in biomedical applications such as cartilage regeneration. However, most DN gels synthesised by usual radical polymerisations are non-biodegradable, and they are not desirable for replacing living tissues in the human body. In this study, we developed a DN gel with polyelectrolyte stents (St-DN gel) that exhibited high mechanical strength and biodegradability under physiological conditions. These degradable St-DN gels were prepared using poly(N,N-dimetylacrylamide) (PDMAAm) as the second network and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) as the first network. The PEG gel contained the molecular stent and a degradable ester bond in its network strands. To prepare the degradable PDMAAm gel, we designed a hydrolysable cross-linking agent, PEG-di(methacryloyloxyethyl succinate) (PEG-DMOS), with six ester bonds. The obtained St-DN gel showed an extremely high compressive fracture strength and strain. We also confirmed that the St-DN gel could be gradually hydrolysed under physiological conditions. Thus, this hydrolysable high-strength gel could be potentially used as an implantable biomedical material.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Polymer Networks


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...