A mechanistic study of thiol addition to N-phenylacrylamide†
Abstract
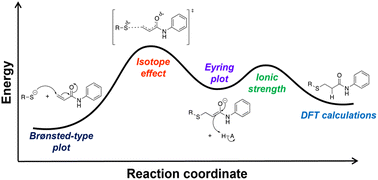
Cysteine (Cys) residues contain a redox-sensitive thiol and are commonly found in enzyme active sites. In recent years, the presence of a reactive thiolate group on a protein has been exploited in the development of irreversible enzyme inhibitors as therapeutic agents. Many targeted covalent inhibitors (TCIs) are designed to covalently react with a specific Cys residue on a target protein active site, irreversibly modifying the target and inhibiting its normal function. The electrophilic warhead most commonly used in this way is the acrylamide functional group. Although the acrylamide group is well known for its ability to undergo thiol-addition reactions, very few studies have been conducted to elucidate the detailed mechanism of this reaction, which inspired us to conduct a thorough kinetic investigation. First, we developed a robust kinetic assay to accurately monitor reaction progress between N-phenylacrylamide (NPA) and a small library of alkyl thiols having widely varying pKa values. This allowed us to construct a Brønsted-type plot for the thiol addition reaction, revealing a βnucRS− value of 0.07 ± 0.04. We also studied the solvent kinetic isotope effects (SKIEs), pH dependence, and temperature dependence of the reaction, which showed that reaction has a relatively large negative ΔS‡, and a small ΔH‡. Computational studies provided a structure for the transition state that is consistent with the experimental data. All of these data are consistent with rate-limiting nucleophilic attack, followed by rapid protonation of the enolate, corresponding to the microscopic reverse of the E1revcb elimination mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...