Degradation of mirubactin to multiple siderophores with varying Fe(iii) chelation properties†
Abstract
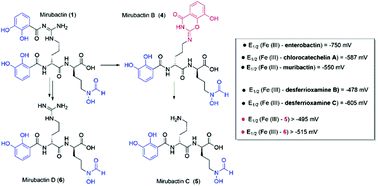
Three siderophores mirubactins B–D (4–6) were identified as the degradation products of previously isolated mirubactin (1). Their structures were revealed by HR-ESI-MS/MS, NMR analyses, and density functional calculations, among which 4 contains an unusual cyclic amidine functionality. Cyclic voltammetry showed that 5 and 6 have reduced iron complexing capacity. Mirubactin (1) and Fe(III) could also form a stable complex, which may be an ingenious approach to compete for iron acquisition by the producing organisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...